What is Flash Crash, what are the causes and consequences of this phenomenon?
A flash crash is a sell-off in a stock or other exchange-traded asset that causes the price to drop by hundreds of points in a very short time.

Often, during a Flash Crash, the price drop occurs so quickly and unexpectedly that many traders perceive this event as an error on the trading platform.
And they begin to search for the reason for such an event on the Internet or contact their broker's customer support.
In fact, their assumptions often turn out to be not so far from the true reasons that cause Flash Crash.
What causes Flash Crash?
Human error - The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has named humans as the main cause of periodic crashes in the stock and currency markets.
Computer and software problems can cause dimensionality in data coming from markets or exchanges, and incorrect price data can also be received due to data processing failures:
In addition, errors in the software code of automated trading systems also have negative consequences.
The scam , a practice known as "Spoofing," involves placing large grids of sell orders into the market that are cancelled when the price approaches.
The U.S. Commodity and Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) believes that fraud was the cause of the S&P 500's flash crash in 2010.
High-frequency trading (HFT) - HFT is a controversial trading method in which an automated system controlled by algorithms, called high-frequency trading .
HFT systems place a large volume of orders into the market at lightning speed, thereby causing negative price movement.
While the role of HFT firms is controversial, central banks believe that HFT firms increase the risk of a Flash Crash.
The biggest examples of Flash Crash in global markets
NYSE Flash Crash of 2010
The NYSE Flash Crash was a sudden crash of the US stock market on May 6, 2010, causing the Dow Jones Industrial Average to fall 1,000 points in just 10 minutes before recovering shortly after:
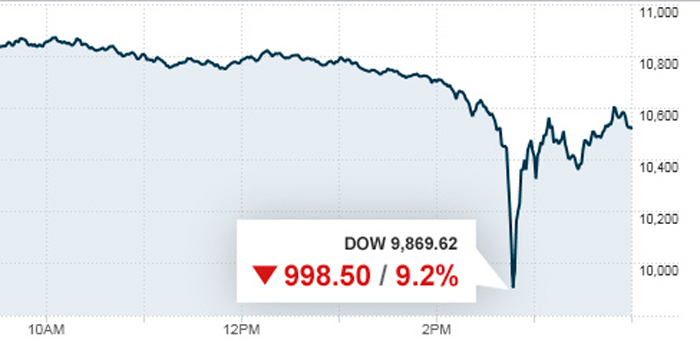
During this event, many stocks on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) fell to $1 or lower.
By the end of the day, the Dow Jones index had recovered to 70% of its initial value.
According to the police investigation, the culprit behind the sell-off was Englishman Navinder Sarao. Investigators discovered that Sarao executed and cancelled hundreds of E-mini S&P futures contracts.
He used illegal trading tactics that forced Waddell & Reed to terminate a $4.1 billion contract.
CME Group warned Sarao and his broker, MF Global, that Sarao's trades were fraudulently manipulating market prices by creating false prices.
Initially, most market participants assumed that the collapse was caused by the high probability of a Greek default, which would lead to a stock market crash. However, the real cause turned out to be the actions of Navinder Sarao.
Flash Crash Bond 2014
On October 15, 2014, the yield on the 10-year Treasury note fell from 2.0% to 1.873% in just a few minutes, before quickly recovering. This marked the biggest drop in the bond market since 2009
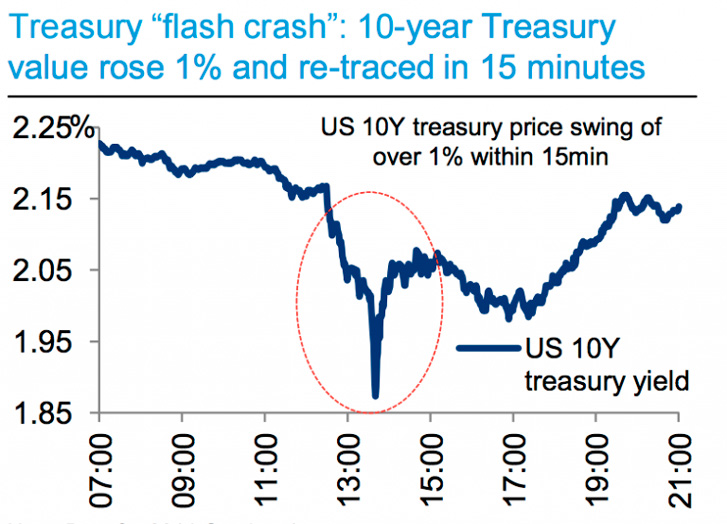
Many blame algorithmic bots for this, as 60% of transactions are made electronically rather than over the phone.
This made the computer system almost unable to respond to large blocks of transactions, leading to Flash Crash.
NASDAQ Flash Crash
The NASDAQ is famous for its flash crash on August 22, 2013. The exchange was suspended from 12:14 PM to 3:25 PM ET:

One of the NYSE servers was unable to contact the NASDAQ server to provide stock price data. Despite numerous efforts, the problem could not be resolved, and the NASDAQ server crashed.
It was this NASDAQ error that led to losses totaling $500 million, around the time Facebook's first IPO was announced on May 18, 2012. As a result, the IPO was delayed by 30 minutes.
The glitch simply prevented orders from being placed, modified, or canceled. After the glitch was resolved, 460 million shares were successfully sold.
How does the Flash Crash affect financial markets?
One of the main consequences is that when a sudden crash occurs, it leads to a recession.
A stock market crash signals a loss of confidence in the economy. When confidence fails to recover over a long period, it leads to a recession.
However, investors believe that the Flash Crash is simply a technical glitch, rather than a loss of investor confidence in the market.
But if this situation continues long enough, it will cause anxiety and negatively impact market confidence.

