Forex market patterns
The main patterns of Forex include stereotypes of exchange rate behavior in similar situations, observing which one can determine the direction of a transaction in advance.

This approach makes it possible to significantly increase profits from transactions.
Forex patterns are frequently repeating events that cause the same reaction in the exchange rate and, when detected, allow one to predict the future trend movement.
This aspect can be discovered independently; it's enough to simply conduct a detailed analysis of trend fluctuations over the course of a week or month. Any price change always has its cause, and sometimes the situation repeats itself with enviable consistency.
By carefully studying the history of the market, one can identify a number of patterns based on such factors as trading sessions, minimum and maximum points, price channels, the occurrence of gaps, and correlations between currency pairs and certain commodity groups.
Description of patterns and their use in Forex trading
1. Price channels – if you notice that the price has repeated previous highs and lows several times over a period of time, a price channel has formed. In this case, a clear pattern in Forex price movement is observed, allowing you to accurately determine your entry point.
2. Closing gaps – very often, after the weekend, gaps form between the closing price and the opening price of the session on the currency exchange, resulting in a certain gap in quotes.
Statistics show that in most cases this gap will definitely close within a day.
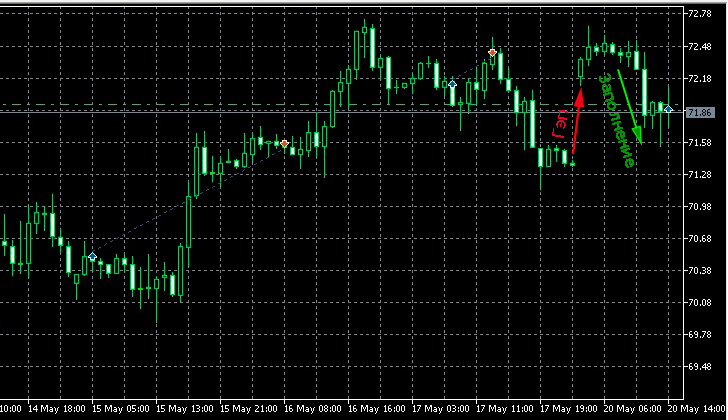
3. Movement and rollback - with sharp price movements, a reverse rollback occurs, and the following trend is always observed: the stronger the price movement or fall, the more pronounced the correction will be.
Many people make money both on the main trend and on its correction.
4. Supply and Demand – the forex market operates according to general economic laws, so an increase in supply or demand for a given currency always causes a change in the exchange rate. Increased demand increases the price, while excess supply leads to a decrease.
5. Expectation of news also influences the rate, just like the news itself – if forecasts for expected indices or important decisions are known, the rate will definitely move in the direction of the news and can only change direction if these expectations are not confirmed.
6. Sessions – the beginning and end of the European session more often end with the euro rising than falling. Similar patterns can be observed in other sessions; they are revealed by monitoring price behavior.
7. Correlation – most currencies react strongly to changes in the prices of commodities such as gold, oil, and agricultural products. To identify this correlation, simply compare currency exchange rates and price changes for a specific group of commodities and determine whether the correlation is direct or inverse.
8. Spread size – there is another Forex rule: the lower the liquidity of a currency pair and the lower the trading activity on it, the larger the spread, so be careful when placing pending orders.
This relationship can lead to unplanned losses, as the spread widens by tens of points at times.
9. Seasonal exchange rate fluctuations – it has been observed that most popular currencies are subject to seasonal exchange rate fluctuations; sometimes the direction of price movement on charts for different years is practically the same.
In conclusion, I'd like to note that the most effective Forex patterns will always be those you identify yourself, so analyze and compare; perhaps you'll notice something that professional traders typically overlook.
Using the Forex principles described above, you can easily create your own simple trading strategy, which can actually be quite effective.

