The current situation in the European economy
Understanding the current state of the EU economy helps in making important decisions, such as investing in European company shares or buying euros.

The European Union, like most other countries worldwide, has recently been experiencing difficult times. The pandemic and rising energy prices are the main causes of the current economic situation.
Record inflation has led to higher interest rates , taking the European Central Bank's key interest rate to 4.5%, the highest level since the euro's inception.
The eurozone economy stalled or even contracted in the third quarter of 2023 under the combined burden of interest rate hikes.

European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde warned that after ten rate hikes, financial conditions are tightening to an unprecedented level. She previously told European Union leaders that the economy would likely stagnate in the coming quarters.
The Germans and Austrians damaged the painting
Lagarde's statement is optimistic compared with forecasts from Barclays economists, who believe the eurozone could fall into recession much sooner.
"The tightening of monetary policy is creating quite a lot of pressure, and we haven't yet seen the full impact," Silvia Ardagna, head of European economic research at the British bank, told Bloomberg Television. "We think core and headline inflation will return to 2% sooner than the ECB forecasts, and that's because we have a much weaker outlook for economic activity.".
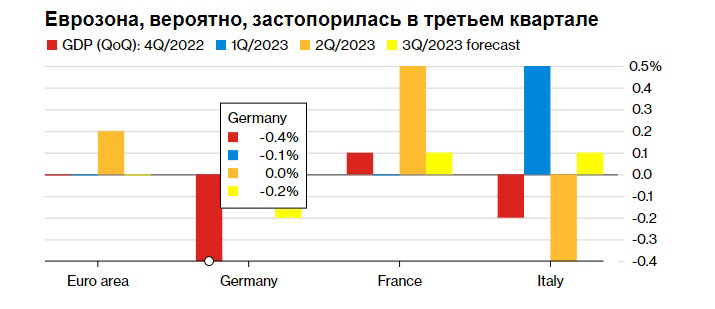
Germany, whose GDP data will be published on Monday, along with Austria and Belgium, exerted the strongest pressure on the eurozone in the third quarter. Meanwhile, data from France and Italy are likely to be more positive.
Preliminary reports from other countries in the region released on Friday, October 27, were mixed, with Spain seeing solid growth during the quarter and Ireland's economy experiencing a noticeable contraction.
Inflation is slowing down
The ECB's leadership is optimistic and hopes for an improvement in inflation figures. The overall rate is expected to reach 3.1%, which is already close to the 2% target.
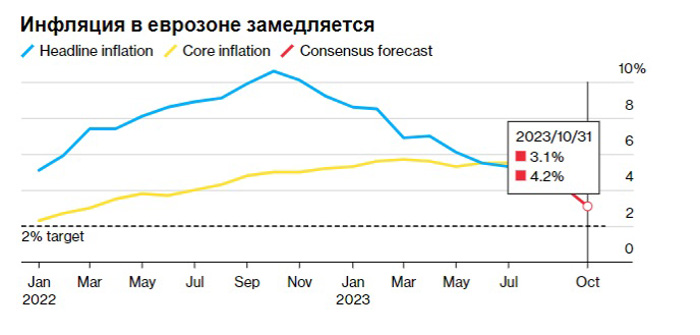
Record interest rates have helped curb inflation, but maintaining high rates is also causing significant damage to the economy. Therefore, once the 2% target is reached, the ECB will decide to cut the interest rate.

